Select menu: Stats | Regression Analysis | Logistic Regression
Use this to fit models to binomial data using logistic regression. Each unit of data thus involves observing a set of subjects, and counting the number of “successes”.
- After you have imported your data, from the menu select
Stats | Regression Analysis | Logistic Regression. - Fill in the fields as required then click Run.
You can set additional Options then after running, you can save the results by clicking Save.
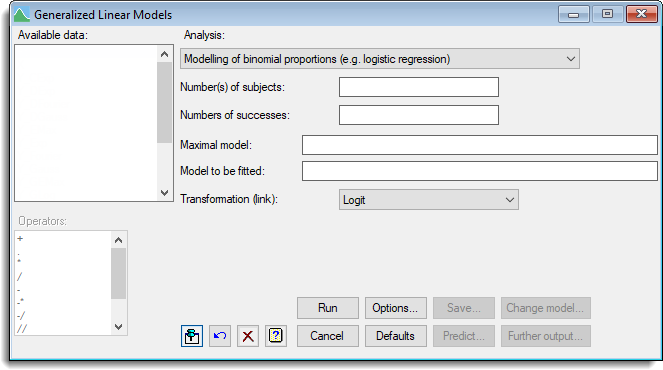
Number of subjects
The numbers of subjects in each set can be defined by entering a variate into the Number(s) of subjects field. The number of subjects corresponds to the Binomial totals field in the General Model analysis when a binomial distribution has been selected. This can be selected from the Available data field. Alternatively, if all the sets had the same number of subjects, you can enter a number or scalar into the field.
Number of successes
The number of successes in each set is specified by entering a variate into the Numbers of successes field; this can again be selected from the Available data field. The number of successes corresponds to the response variate field in the General Model analysis when a binomial distribution has been selected.
Maximal model
Maximal model lets you specify the most complicated model that you are likely to want to consider. It may be left blank, but this may lead to subsequent inability to compare models because of data that are missing for some explanatory variates but not for others.
Model to be fitted
The model to be fitted is specified by entering a model formula into the Model to be fitted field. The formula can involve both variates and factors which can be selected from the Available data list, and operators from the Operators list.
Transformation (link)
By default, linear models are fitted to the probabilities on the Logit scale, however, you can select either the Probit or Complementary log-log transformations to use instead.
Action buttons
| Run | Run the analysis. |
| Cancel | Close the dialog without further changes. |
| Options | Opens a dialog where additional options and settings can be specified. |
| Defaults | Reset to the default settings. Clicking the right mouse on this button produces a shortcut menu where you can choose to set the options using the currently stored defaults or the Genstat default settings. |
| Save | Opens a dialog where you can save results from the analysis. |
| Predict | Lets you calculate predictions based on the current regression model. |
| Change model | This changes the current model by adding or dropping explanatory terms, thus allowing a sequence of models to be fitted and assessed. If you specified a maximal model, all new terms must have appeared in that model. If you did not specify a maximal model and a term is introduced with a missing value for a unit previously used in the regression, the model sequence is interrupted and information will be available only for the current model (excluding that unit) and the new model. |
| Further output | Lets you display additional results and graphical output from the analysis. |
Action Icons
| Pin | Controls whether to keep the dialog open when you click Run. When the pin is down |
|
| Restore | Restore names into edit fields and default settings. | |
| Clear | Clear all fields and list boxes. | |
| Help | Open the Help topic for this dialog. |
See also
- Generalized Linear Models for information on general options and other models
- Options for optional settings and display
- Further Output for additional output subsequent to analysis
- Saving Results for further analysis
- Fitted Model for graphical display of the model
- Model Checking for diagnostic plots for model checking