Selects information to be printed by the generalized linear mixed model analysis and controls certain aspects of the method used.
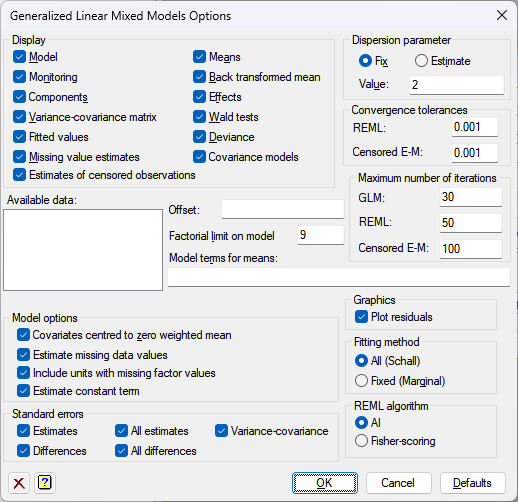
Display
This specifies which items of output are to be produced by the analysis.
| Model | Details of the model that is fitted |
| Monitoring | Monitoring information at each iteration |
| Components | Estimates of variance parameters |
| Variance-covariance matrix | Variance-covariance matrix for the variance parameters |
| Fitted values | Fitted values and residuals from the model |
| Missing value estimates | Estimated values for any missing values in the response variate |
| Means | Tables of means |
| Back-transformed means | Tables of back-transformed means |
| Effects | Estimates of effects |
| Wald tests | Wald tests for fixed model terms |
| Deviance | Deviance (GLM and REML) and information coefficients (AIC and SIC) |
| Covariance models | Estimated covariance models |
Dispersion parameter
Controls whether the dispersion parameter for the variance of the response is estimated from the residual mean square of the fitted model, or fixed at a given value. The dispersion parameter (fixed or estimated) is used when calculating standard errors and standardized residuals. In models with the binomial or Poisson distributions, the dispersion should be fixed at 1 unless a heterogeneity parameter is to be estimated.
Available data
This lists data structures appropriate to the current input field. The contents will change as you move from one field to the next. Double-click a name to copy it to the current input field or type the name.
Offset
A GLMM can be modified to take account of a fixed contribution to the linear effects for each unit, supplied in a variate referred to as the offset.
Model terms for means
This specifies the model terms, as a formula, for which tables of means and/or back-transformed means are displayed. If this field is left blank then all the fixed model terms are displayed.
Maximum number of iterations
Lets you specify the maximum number of iterations of the two fitting cycles in the GLMM algorithm, the GLM fitting and the REML fitting.
Factorial limit on fixed model terms
You can control the factorial limit on fixed model terms to be generated when you use model-formula operators like *. The default is to include all interactions, up to those involving nine variates or factors. (You cannot ask for more than nine.)
Model options
| Estimate missing data values | Specifies whether predictions are formed from the fitted model for missing values of the y-variate; alternatively any units with missing values in the y values are excluded from the analysis. |
| Include units with missing factor values | This specifies whether data units with missing values in any of the factors in the fixed or random models are included in the analysis. |
| Estimate constant term | Specifies whether a constant term is included in the model |
| Covariates centred to zero weighted mean | Controls whether covariates are centred to have zero (weighted) mean for the analysis. |
Standard errors
This specifies which standard errors are to be displayed with the tables of means.
| Differences | Summary of standard errors of differences between means |
| Estimates | Summary of standard errors of differences between means |
| All differences | Full matrix of standard errors between means |
| Variance-covariance | Variance-covariance matrix for the table |
Fitting method
Specifies the method used to form the fitted values. The option All specifies that both fixed and random terms should be used to form fitted values, which gives the method of Schall. The option Fixed indicates that only fixed terms are used to form fitted values which gives the marginal method of Breslow and Clayton.
REML algorithm
The AI (Average Information) method is the standard optimization method for REML in Genstat. It uses sparse matrices and is particularly recommended for large datasets and/or complex models. An alternative method is Fisher scoring which, if selected, also allows an absorbing factor to be specified in the model. This can be used to reduce the time or space requirements when fitting large models with many parameters. A more detailed discussion of the use and choice of absorbing factors can be found in the Genstat 5 Reference Manual.
Action buttons
| OK | Save the option settings and close the dialog. |
| Cancel | Close the dialog without making any changes. |
| Defaults | Reset the options to their default settings. |
Action Icons
| Clear | Clear all fields and list boxes. | |
| Help | Open the Help topic for this dialog. |
See also
- Generalized linear mixed model menu.
- Generalized Linear Mixed Model Save Options dialog
- Generalized Linear Mixed Model Further Output dialog
- Generalized Linear Mixed Model Predictions dialog
- Generalized Linear Mixed Model Permutation Test dialog
- Generalized Linear Mixed Model Residual Plots dialog
- GLMM procedure in command mode for more options
- GLDISPLAY procedure
- GLPREDICT procedure
- GLPERMTEST procedure
- GLPLOT procedure
- GLKEEP procedure