Select menu: Stats | Meta Analysis | Stability Coefficients
To assess new genotypes of plants, trials are often carried out in a range of environments. Yields and other measurements will then be made, and analyses carried out (e.g. using REML) to see how well the genotypes perform. These analyses allow you to determine which genotypes are best overall, or at a specific site. However, they do not consider how reliable, or stable, their yields may be overall. Use this to calculate several stability coefficients to assess this.
- After you have imported your data, from the menu select
Stats | Meta Analysis | Stability Coefficients. - Fill in the fields as required then click Run.
You can set additional Options before running the analysis and store the results by clicking Store.
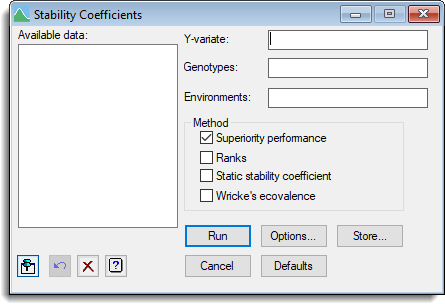
Available data
This lists data structures appropriate to the current input field. It lists variates for use in specifying the y-variate, and factors for the genotypes and environments. Double-click a name to copy it to the current input field or type the name.
Y-variate
Specifies a variate for the data to be analysed.
Genotypes
A factor specifying the genotypes.
Environments
A factor specifying the environments.
Method
Selects the type of method used to calculate the coefficients.
| Superiority performance | This calculates the cultivar-superiority measure of Lin & Binns (1988). For each genotype, this is the sum of the squares of the differences between its mean in each environment and the mean of the best genotype there, divided by twice the number of environments. |
| Ranks | This gives the mean and variance of the ranks of each genotype across the environments where it occurs, as well as the rank-difference coefficient of Nassar & Huehn (1987). For each genotype, this is the sum of the absolute differences between its ranks in all the pairs of environments where it occurs. |
| Static stability coefficient | For each genotype, this is defined as the variance between its means in the various environments. This provides a measure of the consistency of the genotype (but without taking account of how good it is). |
| Wricke’s ecovalence | This is the contribution of each genotype to the genotype-by-environment sum of squares, in an unweighted analysis of the genotype-by-environment means. A low value indicates that the genotype responds in a consistent manner to changes in environment. |
Action buttons
| Run | Run the analysis. |
| Cancel | Close the dialog without further changes. |
| Options | Opens a dialog where additional options and settings can be specified. |
| Defaults | Reset the options back to the default settings. Clicking the right mouse on this button produces a shortcut menu where you can choose to set the options using the currently stored defaults or the Genstat default settings. |
| Store | Opens a dialog to specify names of structures to store the results from the analysis. The names to save the structures must be supplied before running the analysis. |
Action Icons
| Pin | Controls whether to keep the dialog open when you click Run. When the pin is down |
|
| Restore | Restore names into edit fields and default settings. | |
| Clear | Clear all fields and list boxes. | |
| Help | Open the Help topic for this dialog. |
See also
- Stability coefficients options for optional settings and display
- Stability coefficients store options for saving information
- GESTABILITY procedure in command mode