Select menu: Stats | Genetic Models | Individual/Animal Model
Use this to fit single trait genetic models using pedigree information. Models available include those for individual/animals, maternal effects and common environmental effects.
- After you have imported your data, from the menu select
Stats | Genetic Models | Individual/Animal Model. - Fill in the fields as required then click Run.
You can set additional Options then after running the analysis you can save the results by clicking Save.
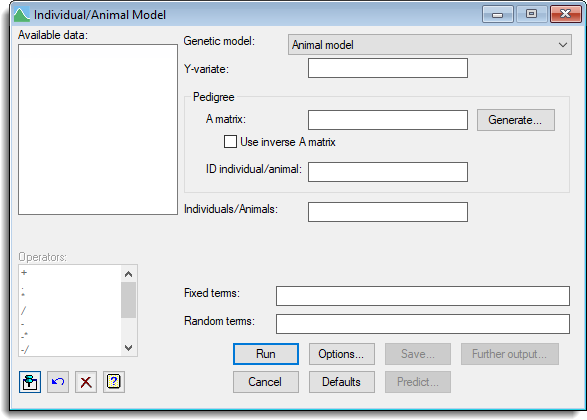
Available data
This lists data structures appropriate to the current input field. Double-click a name to copy it to the current input field or type the name.
Genetic model
Selects the type of genetic model to be analysed.
| Animal model | Fits a single trait individual/animal model where a breeding value is fitted as a random effect. This obtains an estimate of the variance in breeding values which is defined as the additive genetic variance. |
| Maternal trait model | Fits a single trait maternal effects model where a random term is included to model the effects on the offspring trait shared by offspring of the same mother (independent of the additive genetic effects. |
| Common environmental effects model | Fits a single trait common environmental effects model where a random term is included to model environmental effects shared by groups of individuals/animals that are not due to genetic effects. |
Y-variate
Specifies the response variate for analysis.
Pedigree
Specifies a pedigree for the parentage of the animals or individuals.
| A matrix | Specifies the relationship matrix for the pedigree. The values can be supplied within a symmetric matrix or in a pointer to a sparse inverse form. A sparse form of the inverse matrix can be generated by clicking on the Generate button. If the inverse relationship matrix is supplied then select the Use inverse A matrix option. |
| ID Individual/Animal | A factor identifying the individuals/animals within the pedigree. |
Individuals/Animals
A factor identifying the individuals/animals within the pedigree for each value of the trait (y-variate).
Maternal factor
For a maternal trait model this specifies a factor for the mothers of the individuals/animals. The factor must be formed using the same ids as used within the pedigree.
Environment factor
For a common environmental effects model this specifies a factor identifying the different environments.
Fixed terms
The fixed model describes imposed treatment factors and covariates for which the effect of specified levels or values are of interest. The model is described using a formula, which can combine main effects and interactions of factors and also covariates.
Random terms
Allows additional terms to be included in the random model. The random model is generally used to describe those factors for which the values present in an experiment can be considered drawn from some large homogeneous population. The model is described using a formula, which can combine main effects and interactions of factors and also covariates.
Action buttons
| Run | Run the analysis. |
| Cancel | Close the dialog without further changes. |
| Options | Opens a dialog where additional options and settings can be specified for the analysis. |
| Defaults | Reset options to the default settings. Clicking the right mouse on this button produces a shortcut menu where you can choose to set the options using the currently stored defaults or the Genstat default settings. |
| Save | Opens a dialog where you can save results from the analysis. |
| Predict | Allows you to form predictions based on the current model. |
| Further output | Opens a dialog for specifying further output from the analysis and displaying residual and means plots. |
Action Icons
| Pin | Controls whether to keep the dialog open when you click Run. When the pin is down |
|
| Restore | Restore names into edit fields and default settings. | |
| Clear | Clear all fields and list boxes. | |
| Help | Open the Help topic for this dialog. |
See also
- Parental models menu.
- Generating a pedigree menu.
- Linear mixed models menu for mixed model analysis and model building.
- QTL analysis using menus
- REML directive for command mode use of REML.
- VCOMPONENTS directive for further information about fixed and random model terms.