Select menu: Stats | Regression Analysis | All Subsets Regression | Generalized Linear Models
Use this to search through generalized linear regression models.
- After you have imported your data, from the menu select
Stats | Regression Analysis | All Subsets Regression | Generalized Linear Models. - Fill in the fields as required then click Run.
You can set additional Options then after running, you can save the results by clicking Save.
There are various methods for choosing a regression model when there are many candidate model terms. The Change model button on the Generalized Linear Regression dialog provides forward selection, backward elimination and stepwise regression. However these methods result in only one model and alternative models, with an equivalent or even better fit, are easily overlooked. Especially in observational studies with many non-orthogonal terms there are frequently a number of alternative models, and then selection of just one well-fitting model is unsatisfactory and possibly misleading.
A preferable method is to fit all possible regression models, and to evaluate these according to some criterion. In this way a number of best regression models can be selected. However the fitting of all possible regression models is very computer intensive. It should also be used with caution, because models can be selected which appear to have a lot of explanatory power, but contain noise variables only. This may occur particularly when the number of parameters is large in comparison with the number of units. Terms should therefore not be selected on the basis of a statistical analysis alone. This menu can be used to perform these model selection methods.
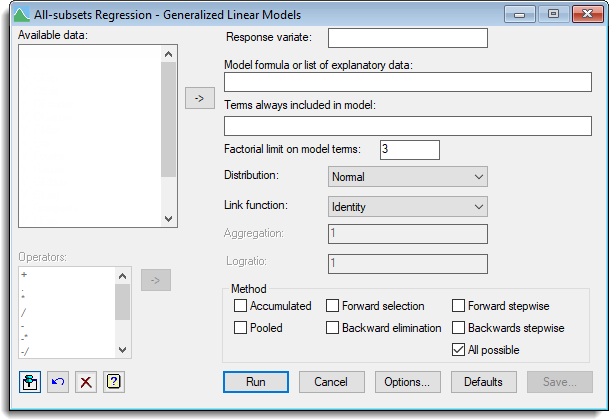
Available data
This lists data structures appropriate to the current input field. The contents will change as you move from one field to the next. Double-click on a name to copy it to the current input field or type the name.
Response variate
Specify a response variate containing the data.
Model formula of list of explanatory data
Specifies the model candidate terms in the fitted model, which may be set using a model formula or using a list of terms separated by commas.
Terms always included in the model
It is sometimes desirable to include specific terms in every model. Such terms may be specified by in this box, which may be set using a model formula or using a list of terms separated by commas.
Operators
This provides a quick way of entering operators in the Model Terms formula. Double-click on the required symbol to copy it to the current input field. You can also type in operators directly. See model formula for a description of each.
Factorial limit on model terms
You can control the factorial limit on model terms to be generated when you use in model-formula operators like ‘*’.
Distribution
List of available error distributions. If you select the Binomial distribution then you must supply the Binomial totals in the space provided. Alternatively, if you select the Negative binomial you must supply the Aggregation in the space provided.
Link function
Lists the available link functions. If you select the Power link function then you must supply the Exponent in the space provided. Similarly, if you select the Logratio link function then you must supply the Logratio in the space provided.
Binomial totals
For a binomial distribution, this specifies a variate which contains the number of units the response was obtained from. This values in this must be greater than or equal to the corresponding values in the response variate.
Method
Specifies the model selection methods to be used.
| Accumulated | An accumulated analysis of deviance in which all model terms are added one by one to the model in the given order |
| Pooled | An accumulated analysis of deviance in which terms with the same number of identifiers, e.g. main effects or two-factor interactions, are pooled |
| Forward Selection | An accumulated analysis of deviance resulting from forward selection |
| Backwards elimination | An accumulated analysis of deviance resulting from backward elimination |
| Forward stepwise | An accumulated analysis of deviance resulting from stepwise regression starting with no candidate terms in the model |
| Backward stepwise | An accumulated analysis of deviance resulting from stepwise regression starting with all candidate terms in the model |
| All possible | Summary statistics for a number of best models among all possible models |
See also
- All Subsets Regression – Generalized Linear Models Options
- All Subsets Regression Save Options
- All Subsets Regression – Linear Models for model selection for Linear Models
- RSEARCH procedure in command mode