You can copy columns from other files directly into the spreadsheet you are working with or add them into a new sheet in your book. The source columns must contain data that is compatible with your current spreadsheet: for example, the columns must be of equal length as those in your current spreadsheet.
- The menu Spread | Add lets you add copied columns into your open spreadsheet:
- The menu Spread | New creates a new spreadsheet in your book and copies the columns into this.
Additionally you can append data columns from a book into a single spreadsheet or stack repeated measurements to combine them into a single column.
You can copy columns from another Genstat file or from a foreign file format. The copied columns must be the same length as those in your current spreadsheet.
If the first row contains text values these will be used as column names in the Genstat spreadsheet, otherwise default column names will be generated (this behaviour can be modified using the options on the dialog).
Column names ending in an exclamation mark (!) will have this character removed and the column will be loaded as a factor. Similarly, column names ending with a dollar $ or a hash # will be copied over as text or variates respectively. Column names must start with a letter (A-Z, a-z or %), and can only contain letters, numbers, a percentage symbol % or an underscore. Genstat will automatically modify any column names that include invalid characters.
- In the source file, use Ctrl+C or another method to select and copy columns to the Windows clipboard.
- Open the spreadsheet you want to copy to columns to then:
To add the columns directly into your spreadsheet, from the menu select Spread | Add | From Clipboard.
OR
To create a new spreadsheet in your book and add columns to it select Spread | New | From Clipboard.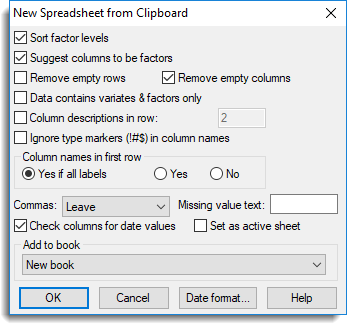
- In the Add to book dropdown list, select your open spreadsheet.
- Set other options as required or leave all settings at their defaults and click OK to insert the columns. (Refer to the New spreadsheet from clipboard options table below for a full description of each option.)
- If your copied data is not tab delimited (separated by tabs) the Text Separator Options dialog will display.
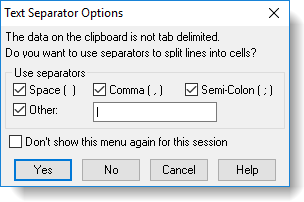
- To use separators set the text separator options as required (see below) and click Yes. To ignore separators click No. Clicking either button will insert your data into the spreadsheet.
- If your copied data is not tab delimited (separated by tabs) the Text Separator Options dialog will display.
| Sort factor levels | If your data contains factor columns this option will sort the numeric levels (or text labels) into ascending order. |
| Suggest columns to be factors | Genstat will prompt you to convert columns to factors when the column contains x number of repeated values. You can set the number of repeated values in Tools | Spreadsheet Options then click the Conversions tab. Select Suggest converting columns with <=x unique items to factors and set the number as required. |
| Remove empty rows | Remove any rows that contain no data. |
| Remove empty columns | By default, any columns that do not contain data are removed from the Genstat spreadsheet. However, you can keep the empty columns by deselecting this option. |
| Data contains variates & factors only | Any column containing text will be converted to either a variate or factor. If the column contains less than 20% text cells, the column will be made into a variate, otherwise the column will be made into a factor. |
| Column descriptions in row | When selected, the cells in the specified row number will be used for column descriptions. |
| Ignore type markers (!#$) in column names | When reading data into Genstat you can append special characters (markers) to the column headers to tell Genstat what data types the columns contain. (The marker ! denotes a factor column, # is a variate and $ denotes a text column.) When you select this option Genstat will ignore the markers and use the contents of the column to decide the column type: columns that contain only numbers will be variates, otherwise they will be designated as text columns |
| Column names in first row | Specifies where to take the column names from.
|
| Commas | This controls how to treat commas in your clipboard data.
|
| Missing value text | This lets you supply your own text to be inserted into empty cells (the default values are an asterisk * for a variate column or a blank cell for factors and texts). For example, you could use N/A to represent a missing value. |
| Check columns for date values | If selected, Genstat checks all text columns to see if they contain data in date format. If any columns appear to contain dates you will be prompted to convert these to a date format. |
| Add to book | Any open spreadsheets will be displayed in this dropdown list. Select your target spreadsheet to insert the data columns into. |
| Date format | This lets you specify a date format for any columns that are read in as dates (a column will be read as a date if the data type marker :D has been appended to the column name). Clicking this button opens a dialog where you can select a date format from the displayed dropdown list or create a custom date format. |
This dialog allows you to specify the separator characters for splitting text into separate cells when creating a spreadsheet from either the clipboard or a text file, or pasting the clipboard to an existing spreadsheet. This dialog will display if the text is not tab delimited.
You can specify the characters to be used as separators by selecting one or more of the following options.
| Use separators | Space – Use a space ‘ ‘ as a separator Comma – Use a comma as a separator Semicolon – Use a semicolon as a separator Other – Enter your own separator characters |
| Don’t show this menu again this session |
Controls whether this dialog is displayed each time you paste data that is not tab delimited, or create a spreadsheet from a text file that does not have tab delimited text. When selected, clicking Yes will ensure that the chosen separators are used to split text until you restart Genstat. If you click No, then the text will not be split in any further operations until you restart Genstat. |
| Yes | Use the specified characters as separators for the data on the clipboard. |
| No | Do not split the text. All the characters on a line will be placed in one cell. |