Select menu: Stats | Mixed Models (REML) | Spatial Models | Irregular Grid
This menu provides facilities for the analysis of one- or two-dimensional data in the form of a grid using the method of residual maximum likelihood (REML), which is also sometimes called restricted maximum likelihood. The data should be supplied in a single variate with variate(s) to specify the Y positions and X positions.
- After you have imported your data, from the menu select
Stats | Mixed Models (REML) | Spatial Models | Irregular Grid.
OR
Stats | Spatial Analysis | Irregular Grid (REML). - Fill in the fields as required then click Run.
You can set additional Options then after running, you can save the results by clicking Save.
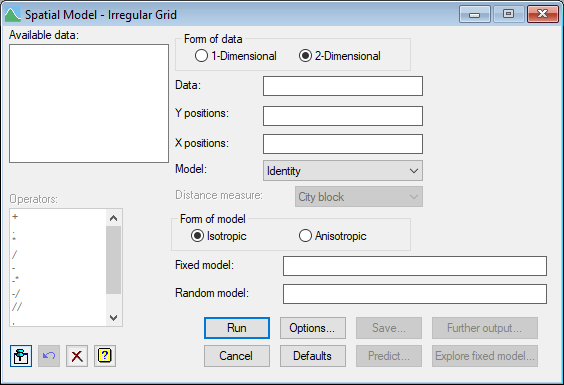
Available data
This lists data structures appropriate to the current input field. The contents will change as you move from one field to the next. Double-click on a name to copy it to the current input field or type the name.
Data
Specifies a variate containing the data values.
Y positions
A variate specifying the Y coordinates in the grid.
X positions
A variate specifying the X positions in the grid. This is only required when you have two-dimensional data.
Model
Lists the available correlation models. Select the correlation model that you want to apply to the grid.
Distance measure
Lists the distance measures that are available for the power correlation model. Select the distance measure that you want to apply.
Form of model
Allows the form of the model to be defined as either isotropic or anisotropic
Fixed model
The fixed model describes imposed treatment factors and covariates for which the effect of specified levels or values are of interest. The model is described using a formula, which can combine main effects and interactions of factors and also covariates.
Random model
The random model is generally used to describe those factors for which the values present in an experiment can be considered drawn from some large homogeneous population. The model is described using a formula, which can combine main effects and interactions of factors and also covariates.
Operators
This provides a quick way of entering operators in the fixed and random model formulas. Double-click on the required symbol to copy it to the current input field. You can also type in operators directly. See model formula for a description of each.
Action buttons
| Run | Run the analysis. |
| Cancel | Close the menu without further changes. |
| Options | Opens a dialog where additional options and settings can be specified for the analysis. |
| Defaults | Set the menu settings back to the default settings. Clicking the right mouse on this button produces a shortcut menu where you can choose to set the options using the currently stored defaults or the Genstat default settings. |
| Save | Opens a dialog where you can save results from the analysis. |
| Predict | Allows you form predictions based on the current model. |
| Further output | Opens a dialog for specifying further output from the analysis and displaying residual and means plots. |
| Explore fixed model | Opens a dialog for exploring the fixed model from the analysis. This allows you try different subsets of the fixed model to see which terms are important |
See also
- Options for specifying output options.
- Further Output for additional output after fitting a model.
- Save for saving the results from a REML analysis.
- Spatial Model – Regular Grid menu.
- REML directive for command mode use of REML, with additional options to control the algorithm and for more sophisticated analyses.
- REML Predictions menu for forming predictions.
- Explore fixed model dialog for exploring which terms are important in the fixed model.