Used to generate an expression. The expression can be constructed step by step by combining data structures and operators. You can use brackets to control the order of evaluation when required. You can also type directly into the expression field. The resulting expression is stored within an expression data structure.
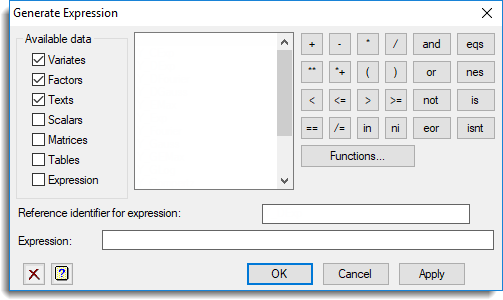
Available data
Lists data structures of the types requested. You can control what data types appear in the available data list by selecting the appropriate type. Double-click a name to copy it into the expression being formed.
Reference identifier for expression
Enter an identifier name to save the expression within.
Expression
Enter the expression. You can either type directly into the box or build an expression using the listed data structure names and operators.
Functions
Enables you to build a function to be inserted into the expression. The function is inserted at the current cursor position.
Keypad
The keypad is used to enter operators into the expression being formed. Click on any button in this diagram for an explanation of its function. You can also type the corresponding text directly into the expression, but note that the logical operators (and, eqs, or, nes, not, is, in, ni, eor, isnt) must be delimited by dots (for example .and.).
See also
- Calculate Functions
- Nonlinear Models Options
- Nonlinear Change Model
- Nonlinear Models Parameter Settings
- Nonlinear Models Reorder Expression List
- Nonlinear Quantile Regression menu
- Standard Curves for information on general options and other curves
- Standard Curves with Correlated Errors menu.
- Exponential Curves
- Fourier Curves
- Gaussian Curves
- Growth Curves
- Rational Curves
- Examples of Standard Nonlinear Curves
- FITNONLINEAR directive
- RCYCLE directive
- MODEL directive
- FITCURVE directive
- FIT directive
- RQNONLINEAR procedure
